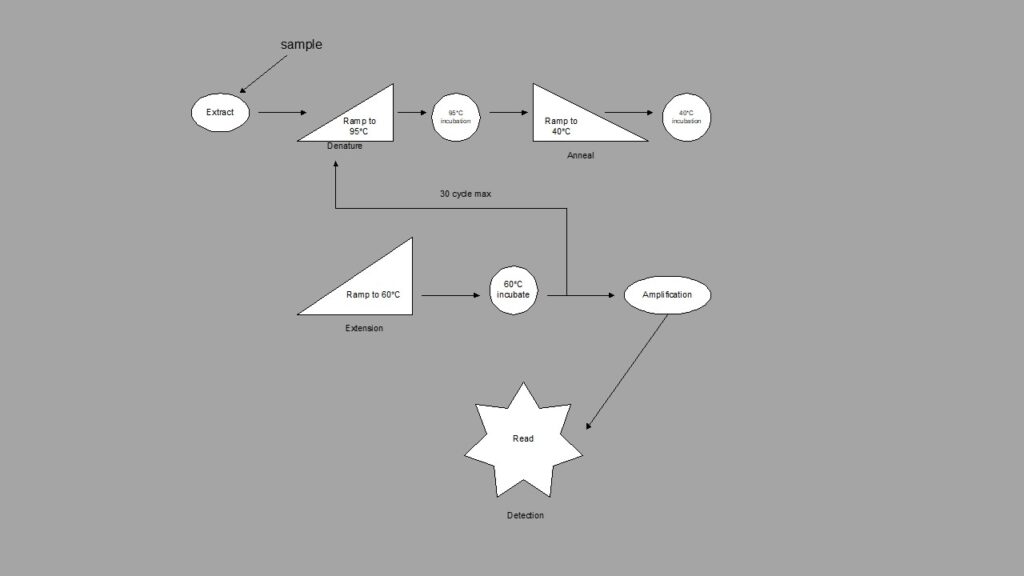
This is the protocol for system operation:
Step 1: Extraction of the DNA from tissue, whole blood or cerebral spinal fluid, and then denatures the cell molecule by ramping up the temperature to near boiling. When the probe and the patient sample hybridize, at 95°C it becomes double-stranded again and re-associates when it incubates at 95°C. The temperature is ramped down to 40°C, and short stretches of nucleotide chains are oligonucleotides called primers anneal to complementary DNA sequences in the target.
After incubation at 40°C, the solution is ramped back up to 60°C where extension occurs (elongation of the growing DNA chain) using the parent DNA strand as the template. This incubates while replication occurs. This process is repeated 20 to 30 times during thermocycling. After thermocycling 20-30 times amplification has occurred and then detection, (read by the Fluorometer) patient result.